The journal entry usually involves a debit to the accounts receivable and a credit to the sales account. Credit sales are recorded both on a company’s income statement and on its statement of financial position or balance sheet. On the income statement, it is recorded under revenue along with cash sales as credit sales are recorded as sales. On the balance sheet, it is recorded as accounts receivable signifying that the amount is owed to the company. A lot of retailers use the credit sales option to purchase goods from manufacturers, generate cash when they sell the merchandise, and then pay off the manufacturers from the sale proceeds.
- In the above example, John Electronics could not make payment by January 30, 2018, and it went bankrupt.
- Businesses must properly record sales credits in order to track their financial success and safeguard the accuracy of their financial statements.
- Dancing Numbers helps small businesses, entrepreneurs, and CPAs to do smart transferring of data to and from QuickBooks Desktop.
- In order to record a sales credit journal entry, businesses need to have an understanding of accrual accounting.
- And, you’re increasing your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Expense account.
Taxation and Finance

In accounting, a credit is an entry that decreases an asset or liability. In a double-entry bookkeeping system, a sales credit journal entry is used to record the decrease in inventory that results from a sale. The journal entry would be debited for the Accounts Receivable and credited for the inventory. A sales credit journal entry record enables businesses to credit the relevant account with the amount due and the specifics of the transaction. Before the start of a financial or assessment period, the technique of documentation is established, and it is followed to prevent confusion in the organization’s recordkeeping system. Later, when the customer does pay, you can reverse the entry and decrease your Accounts Receivable account and increase your Cash account.
Using the Sales and Cash Receipts Journals
The use of a reference code in any of the special journals is very important. Recall that the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger is a record of each customer’s account. An account receivable (AR) is a business’s credit sales that have not yet been collected from its customers. As long as the terms have been agreed upon, companies allow their clients to pay for goods and services over a reasonable period of time. A sales journal entry is a bookkeeping record of any sale made to a customer. The reason is that some transactions do not fit in any special journal.

Cash Sales Journal Entry
The customer is required to make payment to the seller based on the credit term. When cash is collected, the company debits cash account and credit accounts receivable. If you are a business owner, then you know that it is important to keep track of your credit sales. Recording credit sales in a journal entry is simple and can be done in just a few steps. In this blog post, we will go over the steps for recording a credit sale in your journal and how to properly account for it.

- For example, if a business sees a sharp increase in the number of sales credit journal entries, it may be an indication that more customers are buying on credit.
- The credit to the sales account will indicate that the company has earned revenue on the sale.
- In the above example, Walter is offering a 10% discount if Smith makes the payment on or before January 10, 2018.
- It further aids the company management in making the right operational decisions, aids in budgeting, forecasting, and future planning of the company’s finances.
- The total of all of the cash disbursements for the month would be recorded in the general ledger Cash account (Figure 7.27) as follows.
- When companies offer goods or services on credit, they often do so with stipulated conditions for the payment of the amount owed; these conditions are referred to as credit terms.
The general journal is also necessary for adjusting entries (such as to recognize depreciation, prepaid rent, and supplies that we have consumed) and closing entries. In the purchases journal, using the perpetual method will require we debit Inventory instead of Purchases. For a refresher on perpetual versus periodic and related accounts such as freight-in, please refer to Merchandising Transactions.
- Sales journal entries should also reflect changes to accounts such as Cost of Goods Sold, Inventory, and Sales Tax Payable accounts.
- It can also increase the cost of capital cost if customers pay after 15 days or 30 days, depending on their credit terms.
- Credits sales together with cash sales and installment sales compose the net sales of the entity, which is found in the income statement.
- Credit sales are a type of sales in which companies sell goods to the customer on credit based on the credibility of customers.
- However, in this chapter we use the purchases journal for purchases of inventory on account, only.
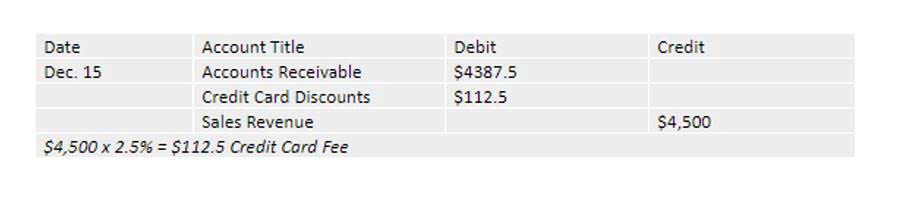
Example of Sales Credit Journal Entry
The sales discount is used to encourage early payment for goods or services received as the discount is often time-bound. The return of products or services by customers results in a fall in revenue, an increase in accounts receivable, or a decrease in accounts payable, depending on whether a refund is given. A sales credit journal entry is a crucial accounting record used to track this. For correct financial reporting and to keep the books of the firm open, these transactions must be properly recorded. That’s because the customer pays you the sales tax, but you don’t keep that amount. Instead, you collect sales tax at the time of purchase, and you make payments to the government quarterly or monthly, depending on your state and local rules.
What is a Sales Credit Journal Entry?
This credit period is usually decided well in advance and can vary from industry to industry. Default on the due date can also lead to penalties or legal proceedings against the defaulter. When youoffer credit to customers, they receive something without paying for it immediately. A current asset whose ending balance should report the cost of a merchandiser’s products awaiting to be sold. The inventory of a manufacturer should report the cost of its raw materials, work-in-process, and finished goods. The cost of inventory should include all costs necessary to acquire the items and to get them ready for sale.

A sales credit journal entry record helps companies credit the respective account with the amount receivable with the details about the transaction. We enter all cash received into the cash receipts journal, and we enter all cash payments into the cash disbursements journal, sometimes also known as the cash payments journal. Good internal control dictates the best rule is that all cash received by a business should be deposited, and all cash paid out for monies owed by the business should be made by check. Money paid out is recorded in the cash disbursements journal, which is generally kept in numerical order by check number and includes all of the checks recorded in the checkbook register. If we paid this month’s phone bill of $135 with check #4011, we would enter it as shown in Figure 7.26 in the cash disbursements journal.